ACM MM 2023
Prompted Contrast with Masked Motion Modeling:
Towards Versatile 3D Action Representation Learning
Abstract
Self-supervised learning has proved effective for skeleton-based human action understanding, which is an important yet challenging topic. Previous works mainly rely on contrastive learning or masked motion modeling paradigm to model the skeleton relations. However, the sequence-level and joint-level representation learning cannot be effectively and simultaneously handled by these methods. As a result, the learned representations fail to generalize to different downstream tasks. Moreover, combining these two paradigms in a naive manner leaves the synergy between them untapped and can lead to interference in training. To address these problems, we propose Prompted Contrast with Masked Motion Modeling, PCM3, for versatile 3D action representation learning. Our method integrates the contrastive learning and masked prediction tasks in a mutually beneficial manner, which substantially boosts the generalization capacity for various downstream tasks. Specifically, masked prediction provides novel training views for contrastive learning, which in turn guides the masked prediction training with high-level semantic information. Moreover, we propose a dual-prompted multi-task pretraining strategy, which further improves model representations by reducing the interference caused by learning the two different pretext tasks. Extensive experiments on five downstream tasks under three large-scale datasets are conducted, demonstrating the superior generalization capacity of PCM3 compared to the state-ofthe-art works.
Key Idea
(1) Mutual Beneficial Design between the Contrastive Learning and Masked Prediction Tasks. The novel views in masked prediction training are utilized as the positive samples for contrastive learning. Meanwhile, contrastive learning provides semantic guidance for masked prediction in turn by propagating the gradients to the prediction decoder.
(2) Dual-Prompted Pre-training Strategy. Domain-specific
prompts and task-specific prompts are introduced for the multi-task pretraining. These trainable prompts enable the model to achieve more discriminative representations for different skeletons.
Framework
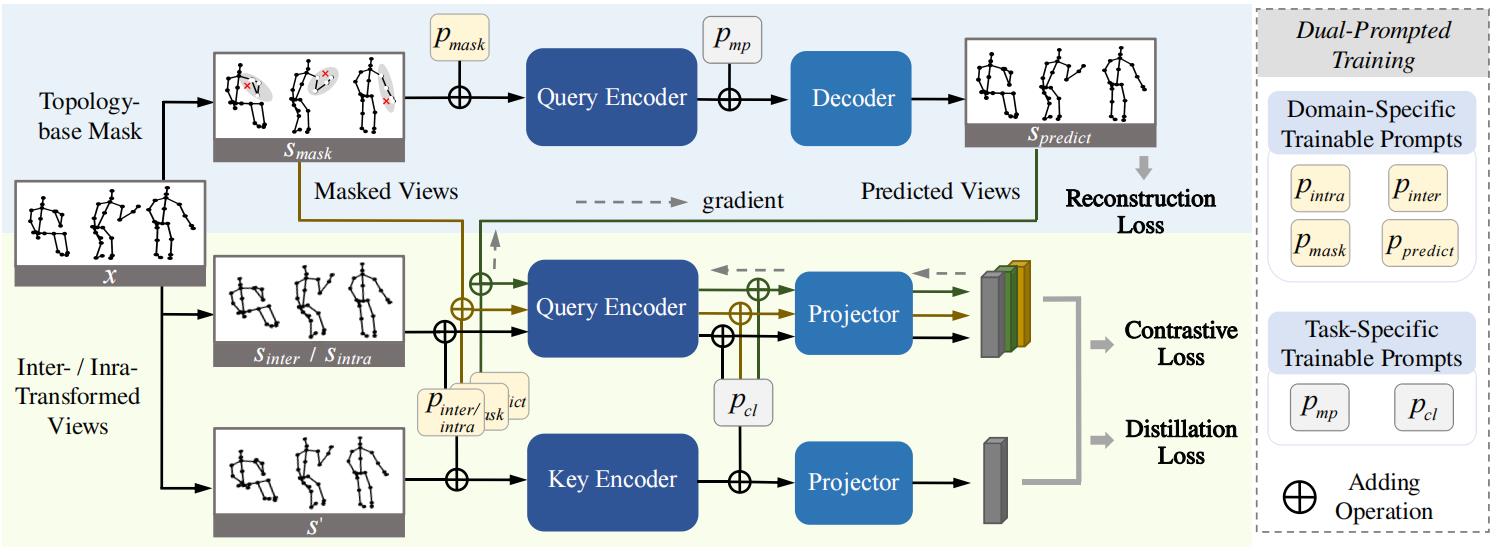
Figure 1. The overview of the proposed method. We integrate the masked skeleton prediction (blue part) and the contrastive learning (yellow-green part) paradigms in a mutually beneficial manner. For brevity, we represent intra- and inter- transformed views in a single branch in the diagram. The masked and the predicted views are utilized to expose more novel motion patterns for contrastive learning. Meanwhile, the gradients from contrastive learning (dotted arrows in figure) are propagated to the masked prediction branch to update the decoder. To further boost the representation learning from different views/tasks, we propose the dual-prompted multi-task pretraining strategy, where domain-specific and task-specific prompts are added in input-wise and feature-wise form, serving as training guidance.
Selected Experimental Results
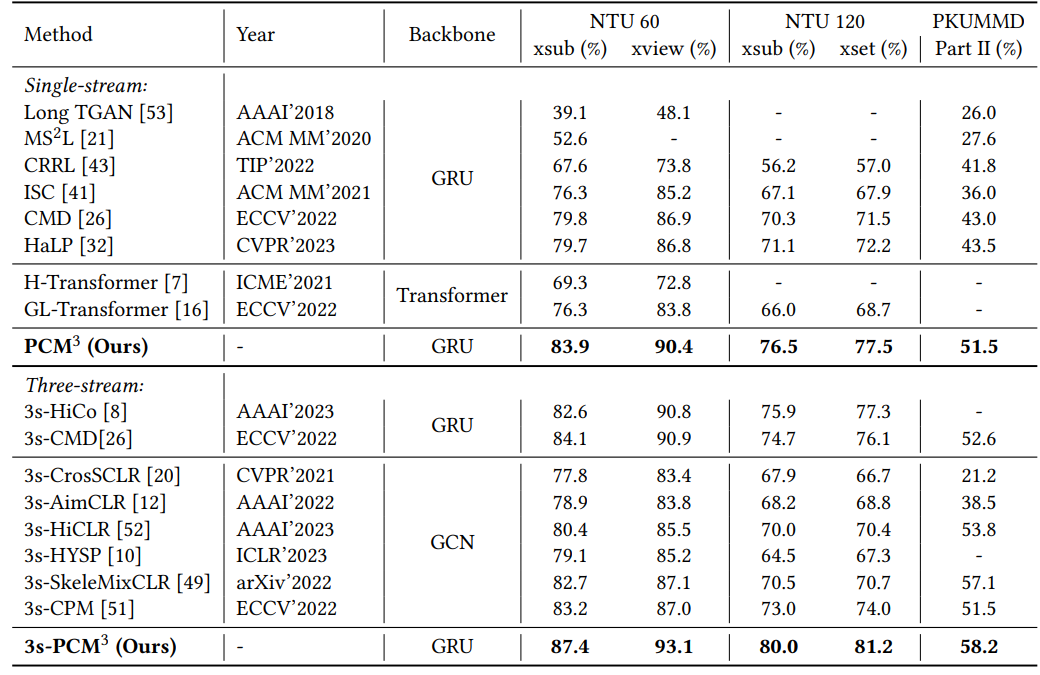
Table 1. Linear evaluation results on NTU60 and NTU120 datasets.
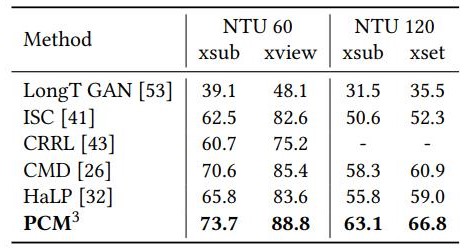
Table 2. Action retrieval results on NTU60 and NTU120 datasets.
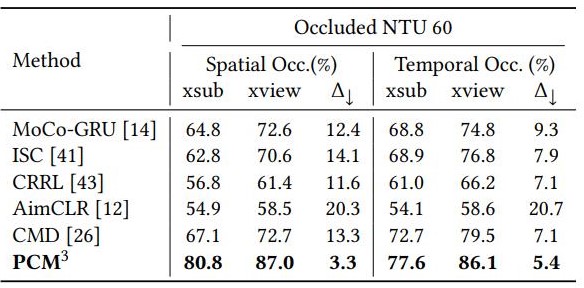
Table 3. Action recognition results with occlusion on NTU60 dataset.
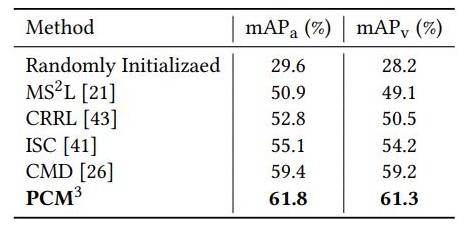
Table 4. Action detection results on PKUMMD datasets.
Citation
@InProceedings{PCM_zhang2023,
author = {Zhang, Jiahang and Lin, Lilang and Liu, Jiaying},
title = {Prompted Contrast with Masked Motion Modeling: Towards Versatile 3D Action Representation Learning},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia},
year = {2023}
}
Reference
[1] Liu, J.; Song, S.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; and Hu, Y. A benchmark dataset and comparison study for multi-modal human action analytics. TOMM 2020.
[2] Shahroudy, A.; Liu, J.; Ng, T.-T.; and Wang, G. NTU RGB + D: A large scale dataset for 3d human activity analysis. CVPR 2016.
[3] Liu, J.; Shahroudy, A.; Perez, M.; Wang, G.; Duan, L.-Y.; and Kot, A. C. NTU RGB + D 120: A large-scale benchmark for 3D human activity understanding. TPAMI 2019.
[4] Guo, T.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Liu, M.; Wang, T.; and Ding, R. Contrastive learning from extremely augmented skeleton sequences for self-supervised action recognition. AAAI 2022.
[5] Lin, L.; Song, S.; Yang, W.; and Liu, J. MS2L: Multi-task self-supervised learning for skeleton based action recognition. ACM MM 2020.