Abstract
In this paper, we study an explicit fine-grained concept decomposition for alignment learning and present a novel framework, Structural Generative Augmentation for 3D Human Motion Retrieval (SGAR), to enable generation-augmented retrieval. Extensive experiments on three benchmarks, including motion-text retrieval as well as recognition and generation applications, demonstrate the superior performance and promising transferability.
Method
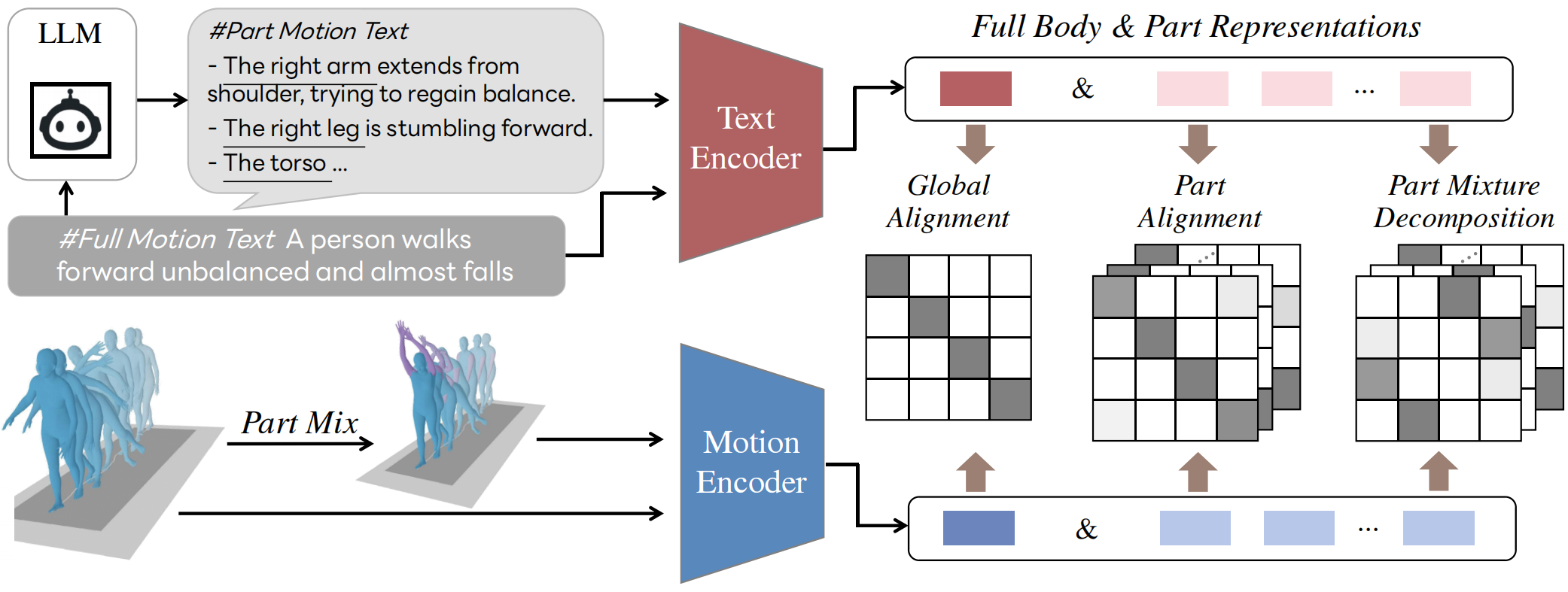
To enable part-based motion alignment, we integrate structural linguistic knowledge from LLMs and propose a part-mixture learning strategy. By decoupling the motion representations of the global body and local parts, our method can facilitate alignment within different structural levels. In addition to independently minimizing the Euclidean distance of embeddings at global and local motion levels, a directional alignment objective is introduced to model the relational knowledge between them. This further alleviates over-fitting and leads to better representation consistency.
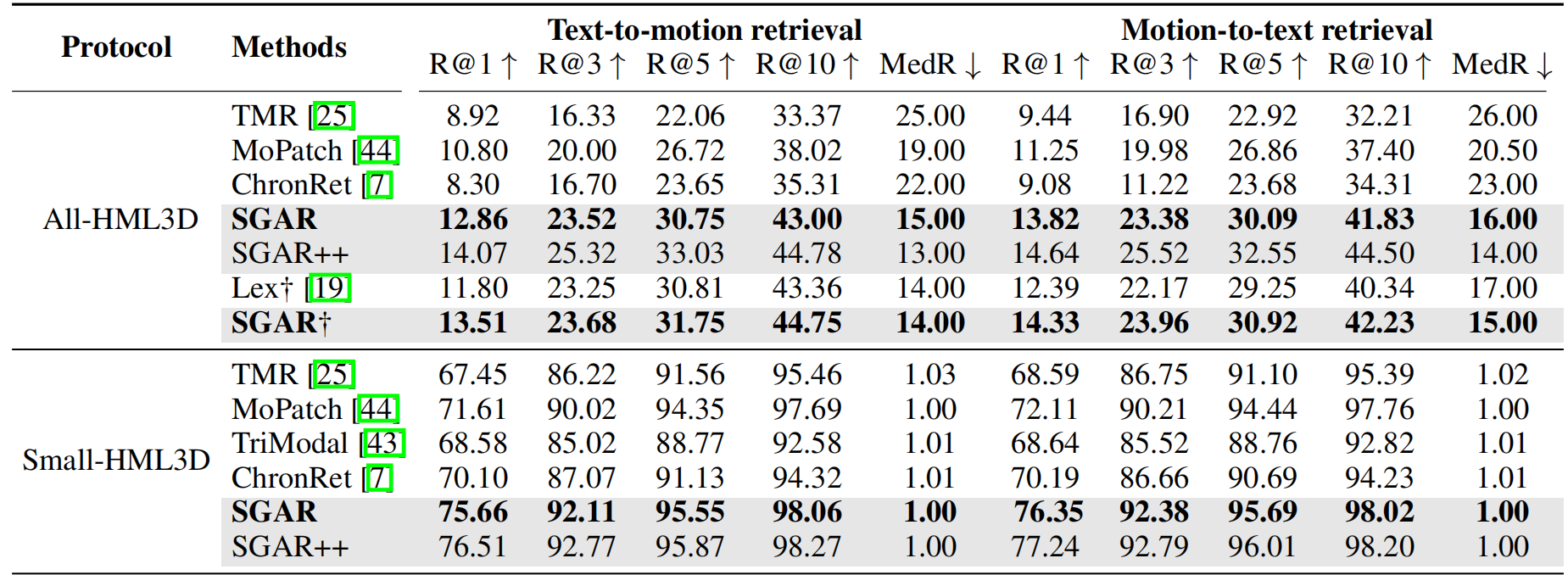
Motion-text retrieval results on HML3D and KIT benchmark.
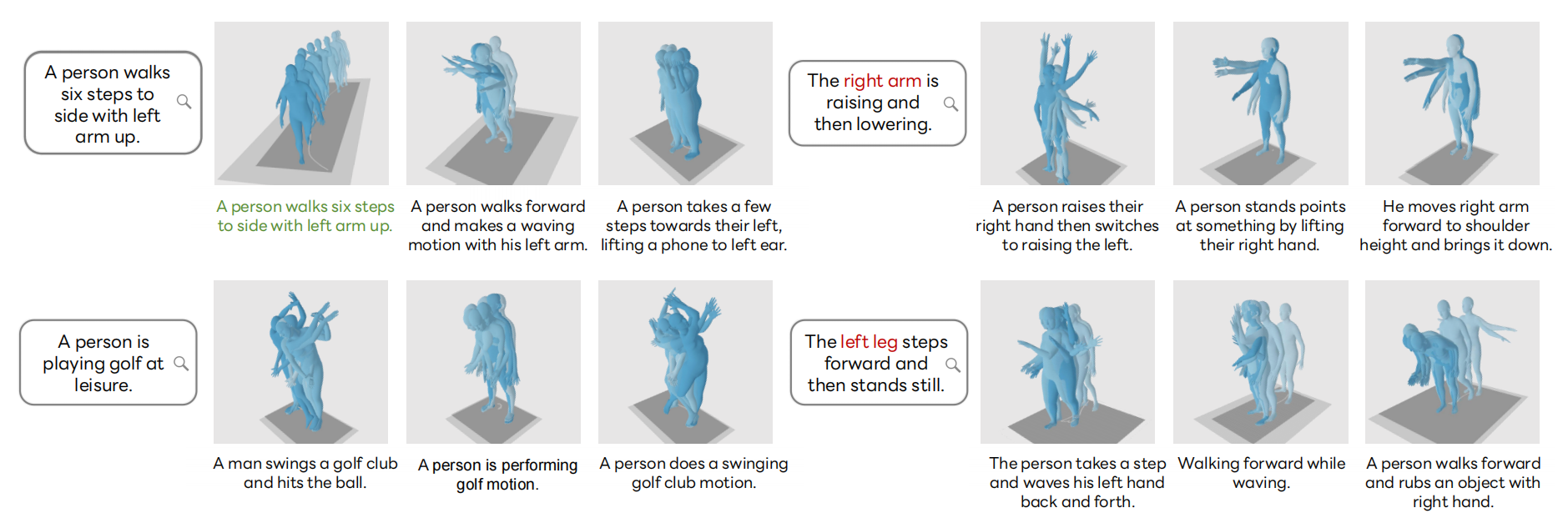
Qualitative T2M retrieval with top-3 results on HumanML3D testing set.
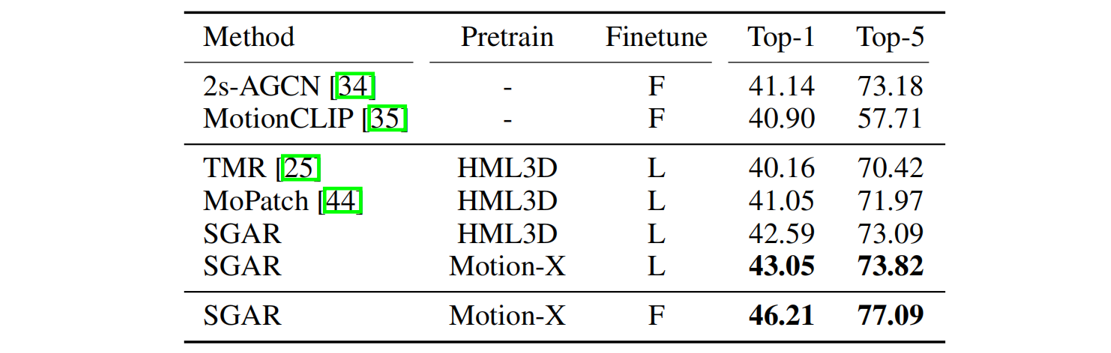
Transfer learning results for action recognition on BABEL benchmark.
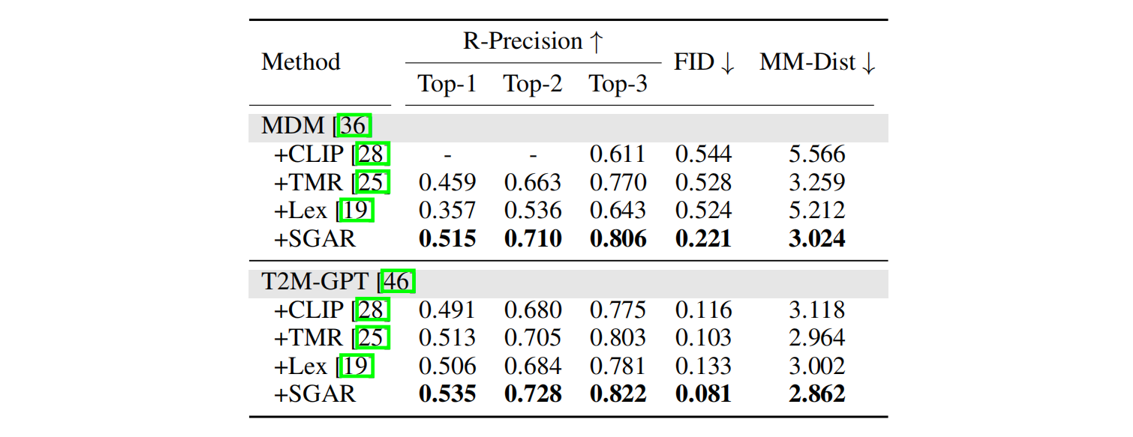
Results of motion generation with different text encoders.
BibTeX
@inproceedings{zhangsgar2024,
title={SGAR: Structural Generative Augmentation for 3D Human Motion Retrieval},
author={Zhang, Jiahang and Lin, Lilang and Yang, Shuai and Liu, Jiaying},
booktitle={NeurIPS},
year={2025}
}